|
|
@@ -94,8 +94,8 @@ Rewrite this section once we have implemented this properly.
|
|
|
\subsection{Transformation}
|
|
|
|
|
|
A simple perspective transformation will be sufficient to transform and resize
|
|
|
-the characters to a normalized format. The corner positions of characters in the
|
|
|
-dataset are supplied together with the dataset.
|
|
|
+the characters to a normalized format. The corner positions of characters in
|
|
|
+the dataset are supplied together with the dataset.
|
|
|
|
|
|
\subsection{Reducing noise}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -141,8 +141,9 @@ by the n(with i=i$_{th}$ pixel evaluated, starting with $i=0$).
|
|
|
This results in a mathematical expression:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Let I($x_i, y_i$) an Image with grayscale values and $g_n$ the grayscale value
|
|
|
-of the pixel $(x_i, y_i)$. Also let $s(g_i, g_c)$ (see below) with $g_c$ = grayscale value
|
|
|
-of the center pixel and $g_i$ the grayscale value of the pixel to be evaluated.
|
|
|
+of the pixel $(x_i, y_i)$. Also let $s(g_i, g_c)$ (see below) with $g_c$ =
|
|
|
+grayscale value of the center pixel and $g_i$ the grayscale value of the pixel
|
|
|
+to be evaluated.
|
|
|
|
|
|
$$
|
|
|
s(g_i, g_c) = \left\{
|
|
|
@@ -236,12 +237,12 @@ noise in the margin.
|
|
|
In the next section you can read more about the perspective transformation that
|
|
|
is being done. After the transformation the character can be saved: Converted
|
|
|
to grayscale, but nothing further. This was used to create a learning set. If
|
|
|
-it doesn't need to be saved as an actual image it will be converted to a
|
|
|
+it does not need to be saved as an actual image it will be converted to a
|
|
|
NormalizedImage. When these actions have been completed for each character the
|
|
|
license plate is usable in the rest of the code.
|
|
|
|
|
|
\paragraph*{Perspective transformation}
|
|
|
-Once we retrieved the cornerpoints of the character, we feed those to a
|
|
|
+Once we retrieved the corner points of the character, we feed those to a
|
|
|
module that extracts the (warped) character from the original image, and
|
|
|
creates a new image where the character is cut out, and is transformed to a
|
|
|
rectangle.
|
|
|
@@ -274,11 +275,18 @@ surrounding the character.
|
|
|
\subsection{Creating Local Binary Patterns and feature vector}
|
|
|
Every pixel is a center pixel and it is also a value to evaluate but not at the
|
|
|
same time. Every pixel is evaluated as shown in the explanation
|
|
|
-of the LBP algorithm. The 8 neighbours around that pixel are evaluated, of course
|
|
|
-this area can be bigger, but looking at the closes neighbours can give us more
|
|
|
-information about the patterns of a character than looking at neighbours
|
|
|
-further away. This form is the generic form of LBP, no interpolation is needed
|
|
|
-the pixels adressed as neighbours are indeed pixels.
|
|
|
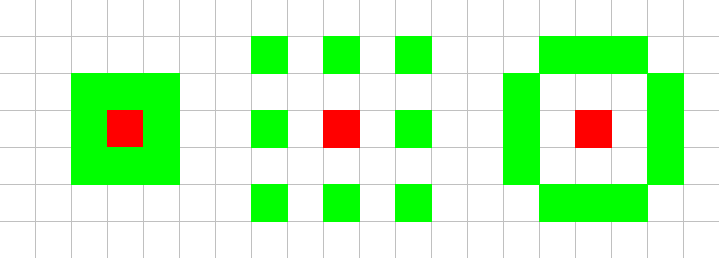
+of the LBP algorithm. There are several neighbourhoods we can evaluate. We have
|
|
|
+tried the following neighbourhoods:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+\begin{figure}[h!]
|
|
|
+\center
|
|
|
+\includegraphics[scale=0.5]{neighbourhoods.png}
|
|
|
+\caption{Tested neighbourhoods}
|
|
|
+\end{figure}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+We chose these neighbourhoods to prevent having to use interpolation, which
|
|
|
+would add a computational step, thus making the code execute slower. In the
|
|
|
+next section we will describe what the best neighbourhood was.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Take an example where the
|
|
|
full square can be evaluated, there are cases where the neighbours are out of
|
|
|
@@ -311,9 +319,10 @@ available. These parameters are:\\
|
|
|
$\sigma$ & The size of the Gaussian blur.\\
|
|
|
\emph{cell size} & The size of a cell for which a histogram of LBPs will
|
|
|
be generated.\\
|
|
|
+ \emph{Neighbourhood}& The neighbourhood to use for creating the LBP.\\
|
|
|
$\gamma$ & Parameter for the Radial kernel used in the SVM.\\
|
|
|
$c$ & The soft margin of the SVM. Allows how much training
|
|
|
- errors are accepted.
|
|
|
+ errors are accepted.\\
|
|
|
\end{tabular}\\
|
|
|
\\
|
|
|
For each of these parameters, we will describe how we searched for a good
|
|
|
@@ -339,7 +348,14 @@ the feature vectors will not have enough elements.\\
|
|
|
In order to find this parameter, we used a trial-and-error technique on a few
|
|
|
cell sizes. During this testing, we discovered that a lot better score was
|
|
|
reached when we take the histogram over the entire image, so with a single
|
|
|
-cell. therefor, we decided to work without cells.
|
|
|
+cell. Therefore, we decided to work without cells.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+\subsection{Parameter \emph{Neighbourhood}}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+The neighbourhood to use can only be determined through testing. We did a test
|
|
|
+with each of these neighbourhoods, and we found that the best results were
|
|
|
+reached with the following neighbourhood, which we will call the
|
|
|
+()-neighbourhood.
|
|
|
|
|
|
\subsection{Parameters $\gamma$ \& $c$}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -351,7 +367,7 @@ different feature vector than expected, due to noise for example, is not taken
|
|
|
into account. If the soft margin is very small, then almost all vectors will be
|
|
|
taken into account, unless they differ extreme amounts.\\
|
|
|
$\gamma$ is a variable that determines the size of the radial kernel, and as
|
|
|
-such blablabla.\\
|
|
|
+such determines how steep the difference between two classes can be.\\
|
|
|
\\
|
|
|
Since these parameters both influence the SVM, we need to find the best
|
|
|
combination of values. To do this, we perform a so-called grid-search. A
|
|
|
@@ -445,7 +461,7 @@ plates. Upon completion all kinds of learning and data sets could be created.
|
|
|
\subsection{How it went}
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sometimes one cannot hear the alarm bell and wake up properly. This however was
|
|
|
-not a big problem as no one was affraid of staying at Science Park a bit longer
|
|
|
+not a big problem as no one was afraid of staying at Science Park a bit longer
|
|
|
to help out. Further communication usually went through e-mails and replies
|
|
|
were instantaneous! A crew to remember.
|
|
|
|